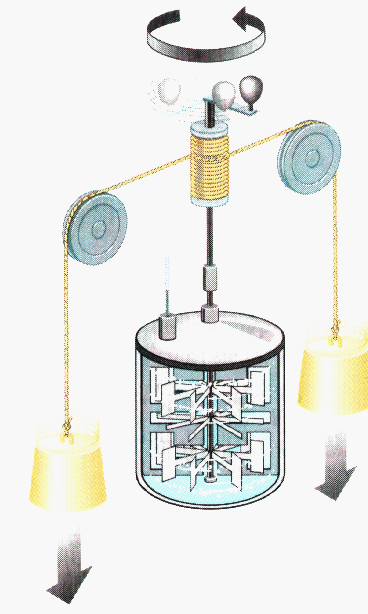

Potential energy is stored energy that depends upon the relative position of
various parts of a system. A spring has more potential energy when it is
compressed or stretched. A steel ball has more potential energy raised above the
ground than it has after falling to the Earth. In the raised position it is
capable of doing more work. Potential energy is a property of a system and not
of an individual body or particle; the system composed of the Earth and the
raised ball, for example, has more potential energy as the two are farther
separated.
..
Potential energy arises in systems with parts that exert forces on each other
of a magnitude dependent on the configuration, or relative position, of the
parts. In the case of the Earth-ball system, the force of gravity between the
two depends only on the distance separating them. The work done in separating
them farther, or in raising the ball, transfers additional energy to the system,
where it is stored as gravitational potential energy.
..
Potential energy also includes other forms. The energy stored between the
plates of a charged capacitor is electrical potential energy. What is commonly
known as chemical energy, the capacity of a substance to do work or to evolve
heat by undergoing a change of composition, may be regarded as potential energy
resulting from the mutual forces among its molecules and atoms. Nuclear energy
is also a form of potential energy.
..
The potential energy of a system of particles depends only on their initial
and final configurations; it is independent of the path the particles travel. In
the case of the steel ball and the earth, if the initial position of the ball is
ground level and the final position is ten feet above the ground, the potential
energy is the same, no matter how or by what route the ball was raised. The
value of potential energy is arbitrary and relative to the choice of reference
point. In the case given above, the system would have twice as much potential
energy if the initial position were the bottom of a ten-foot-deep hole.
..
Gravitational potential energy near the Earth's surface may be computed by
multiplying the weight of an object by its distance above the reference point.
In bound systems, such as atoms, in which electrons are held by the electric
force of attraction to nuclei, the zero reference for potential energy is a
distance from the nucleus so great that the electric force is not detectable. In
this case, bound electrons have negative potential energy, and those just free
of the nucleus and at rest have zero potential energy.
..
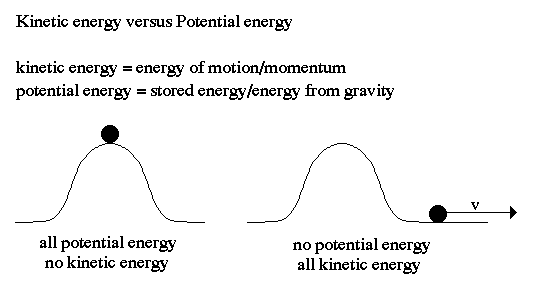
Kinetic Energy :
Potential energy may be converted into energy of motion, called kinetic energy, and in turn to other forms such as electrical energy. Thus, water behind a dam flows to lower levels through turbines that turn electric generators, producing electric energy plus some unusable heat energy resulting from turbulence and friction.
Historically, potential energy was included with kinetic energy as a form of
mechanical energy so that the total energy in gravitational systems could be
calculated as a constant.
..
Excerpt from the Encyclopedia Britannica without permission.